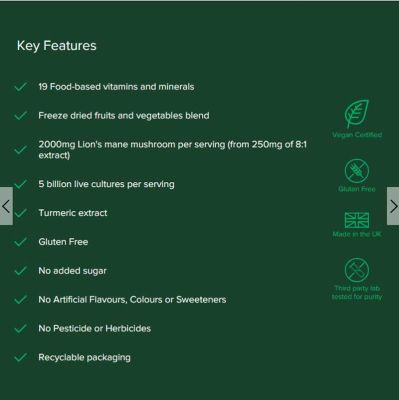
Anti-Inflammatory
What is Inflammation and how is it Caused?
Inflammation is natural and is part of the bodies vital defence mechanism that sets the healing process in action. The body’s white blood cells attack intruders like pathogens or foreign bodies and tries to expel them.
Acute Inflammation – This is the relatively short-lived natural process that generally involves 5 reactions – pain, redness, reduced function, heat and swelling.
Chronic Inflammation – This can continue for months to years. It generally occurs when the body’s defence mechanism becomes hypersensitive and ‘out of control’ to what it perceives as a threat; it is usually triggered and then continues well beyond this to become a debilitating condition. Signs may include swollen joints, pain, and fatigue, and headache, loss of appetite, fever and chills.
Conditions linked to chronic inflammation are heart disease, leaky gut, allergies, and cancer, heart disease, and diabetes, types of arthritis, asthma and Alzheimer’s.
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
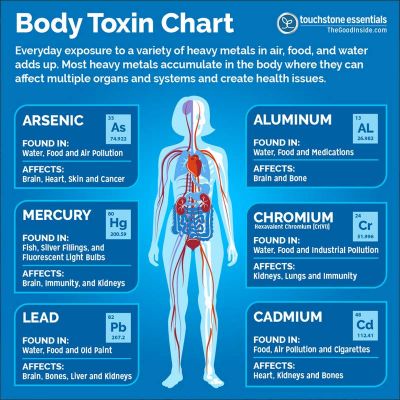
Studies into chronic inflammation have reported links to environmental toxins like cigarette smoke and general pollution, and to an excess of fat in the body due to poor diet that is rich in unhealthy processed foods.
How to Prevent Chronic Inflammation
Diet & Exercise - Reducing intake of processed (often with preservatives and sweeteners), fried and refined-sugary foods can help to prevent inflammation in the body. Eat foods rich in antioxidants and as organic and natural as possible containing healthy fats – include recommended portions of clean protein, fresh fruit and vegetables and whole grains. Try to include exercise at least three times a week to prevent build-up of visceral fat.
Environmental – Prevent inflammation by reducing exposure to cigarette smoke and environmental toxins as much as possible; be aware of the damage they can cause. Ensure your home is aired on a regular basis to prevent build-up of dust and irritation to airways that can be caused by dust-mites. This is especially important in those with asthma, allergies or chronic chest conditions.
Stress & Sleep – These can both impact on inflammation in the body. Reduce stress levels and prevent the over-production of cortisol that leads to persistent inflammation. Sleep deprivation and over-sleeping persistently can activate the inflammatory process so ensure to achieve a balanced sleep pattern.
Supplementation – Consider boosting your potential to reduce chronic inflammation with natural anti-inflammatory supplements in addition to making changes to your diet and lifestyle.







.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)